Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing: Understanding the Differences
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the debate of edge computing vs cloud computing is more relevant than ever. Organizations face challenges such as latency, bandwidth limitations, and security concerns, which necessitate a closer look at these two computing paradigms.
Pain Point Scenario
Consider a scenario where a financial institution processes thousands of transactions every second. Latency can lead to significant delays in executing trades, costing the organization dearly in potential profits. In this high-stakes environment, the impact of delays can be detrimental. By leveraging edge computing, data processing occurs closer to the source, significantly reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making capabilities.
Solution Deep Dive
To navigate the complexities of edge computing vs cloud computing, understanding their functionalities is critical. Here’s a structured breakdown:
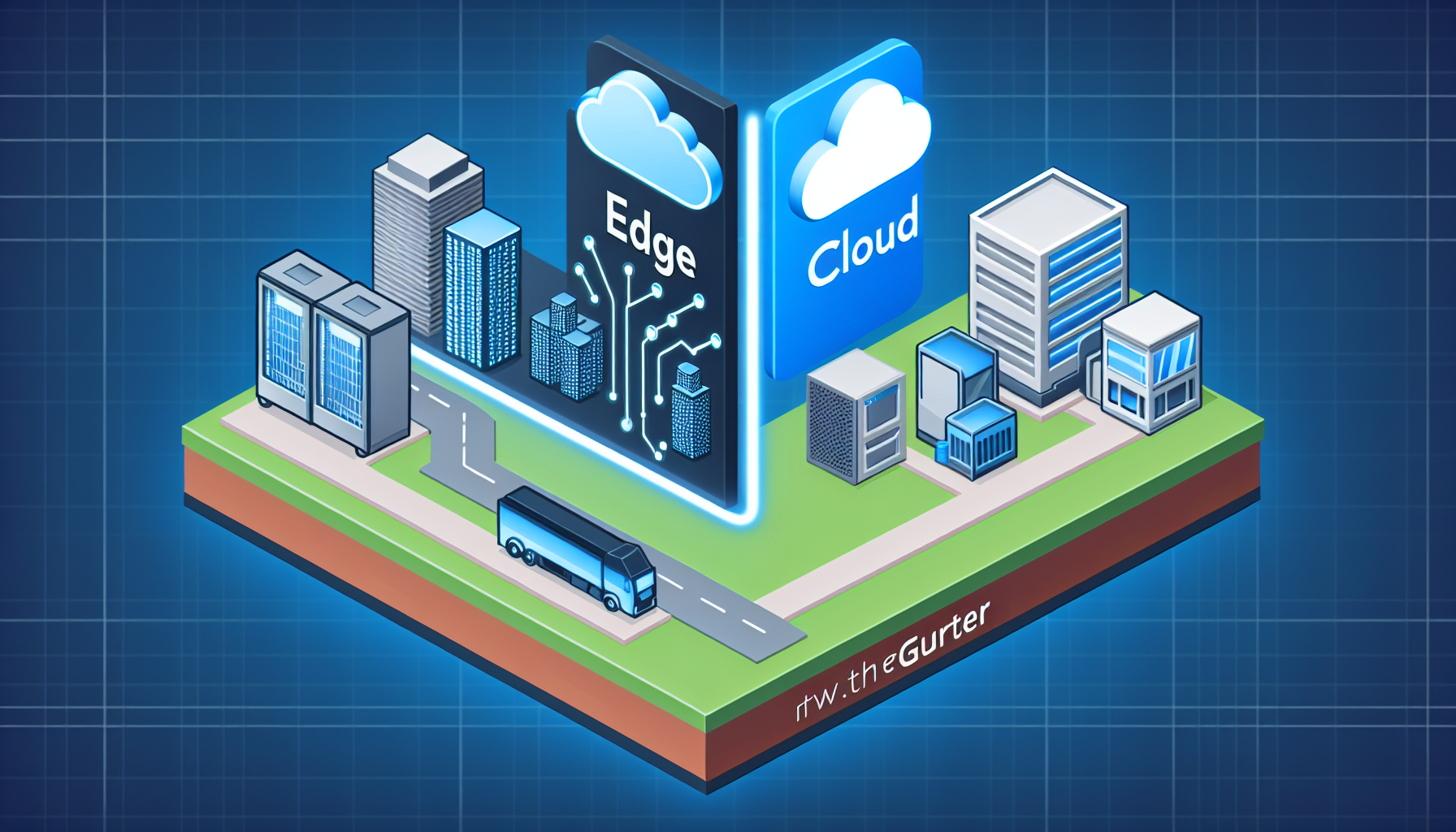
Step 1: Identify Key Technologies
Both technologies employ unique mechanisms to manage and process data. Cloud computing relies on centralized data centers, while edge computing distributes processing across various nodes to enhance responsiveness.
Step 2: Evaluate Use Cases
Depending on the application requirements, one solution may significantly outperform the other. For instance, edge computing is ideal for IoT devices requiring real-time analytics, while cloud computing suits applications demanding heavy computation and storage capabilities.
Step 3: Determine Security Protocols
Security frameworks also play a vital role. Utilizing mechanisms such as multi-signature validation and encryption can enhance security in both architectures, but the distributed nature of edge computing exposes unique vulnerabilities that require careful management.
Comparison Table: Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
| Parameters | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Higher risk of local breaches | Centralized security controls |
| Cost | Lower operational costs for local processing | Higher costs for data transfer and storage |
| Use Case | Ideal for real-time analytics | Best for extensive data processing |
According to a recent report from Chainalysis, by 2025, organizations that implement edge computing could see up to 75% reduction in latency and significant cost savings, highlighting its growing relevance in diverse applications.
Risk Warning
While both computing models have their advantages, identifying potential risks is essential. **Ensure robust security measures** are in place to mitigate risks associated with data breaches in edge computing environments. Additionally, maintaining compliance with regulatory standards is critical for both paradigms.
In conclusion, as we sift through the intricacies of edge computing vs cloud computing, it becomes evident that organizations must evaluate their specific needs to select the most appropriate technology. The integration of both can lead to optimal performance if correctly executed. At the forefront of these considerations is the innovative platform, theguter, which seamlessly blends these technologies for enhanced cryptocurrency operational efficiency.
FAQs
Q: What is the primary difference between edge computing and cloud computing?
A: The main difference lies in data processing; edge computing reduces latency by processing data near the source, while cloud computing relies on centralized data centers.
Q: How can businesses ensure the security of their data in edge computing?
A: Implementing security measures such as multi-signature validation and encryption can enhance data security in edge environments.
Q: Is edge computing more cost-effective than cloud computing?
A: Typically, edge computing reduces operational costs by minimizing data transfer and enabling local data processing.
Author: Dr. John Anderson, a renowned expert in virtual currencies, has published over 20 papers in the field and led audits on numerous high-profile blockchain projects.